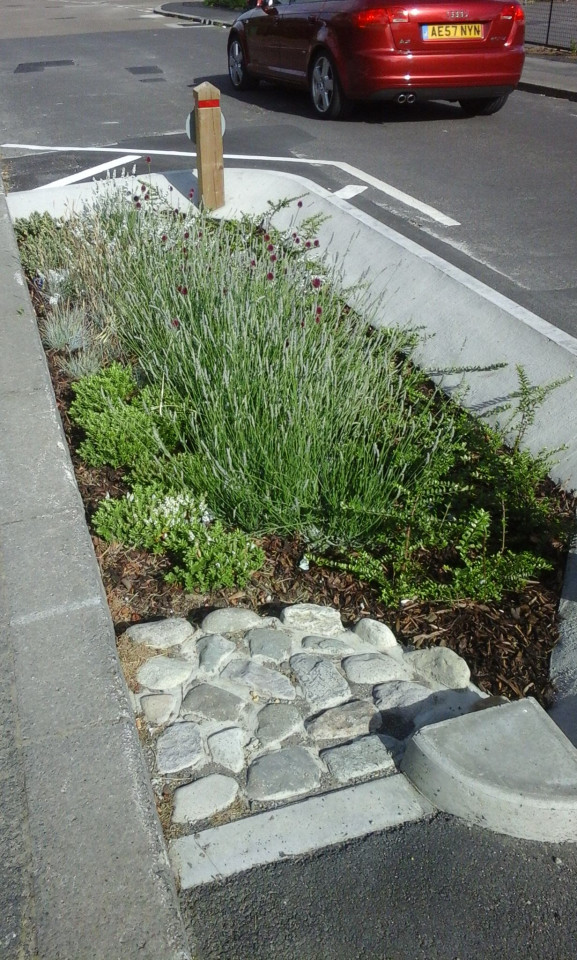
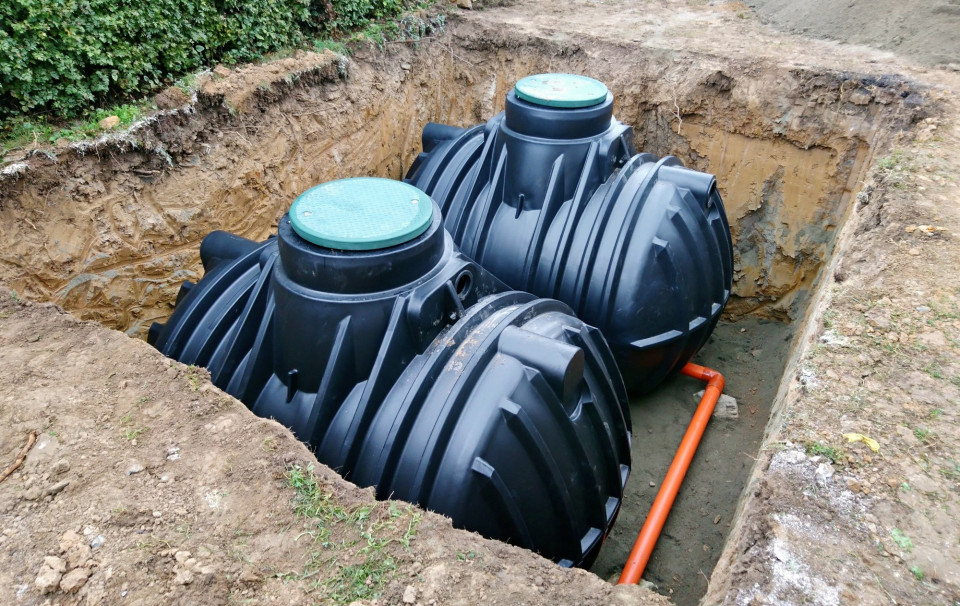
Highway bioretenton pods
Traffic calming measures which decrease water entering the sewer network and offer extra stoarage capacity in heavy flows. Multiple benefits achieved in water quality improvements from highway run off and slowing traffic.
- Category: Structural / Ecosystem-based
- Application Scale: Street
- Sector: Water / Mobility / Social / Health / Environment
- Target: Mitigation
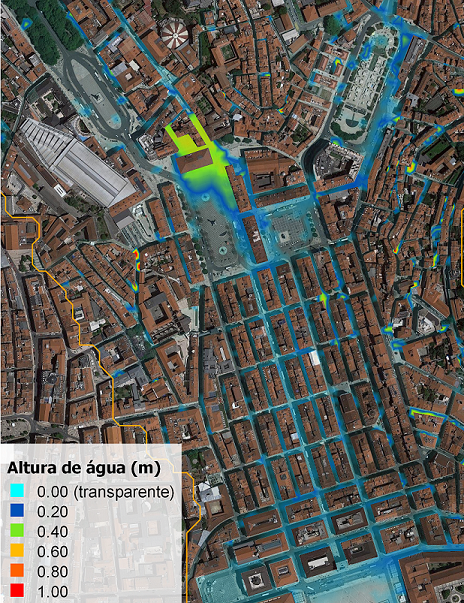
Identify high risk areas by conducting studies involving flood modelling analysis
Carrying out simulations of heavy rainfall events, high tides and high river flows in combination with topographic data and utilising flood modelling software.
- Category: Structural / Technological
- Application Scale: City
- Sector: Water / Mobility / Social / Health / Environment / Emergency
- Target: Adaptation
Identify high risk areas by conducting studies involving modelling analysis
Use of computational modelling tools to simulate rainfall events and city services' reaction. Useful models include drainage system and superficial runoff simulations tools. Better approaches include integrated and multisectorial simulating tools.
- Category: Non-structural / Informational
- Application Scale: City
- Sector: Water / Mobility / Telecom / Social / Power / Waste / Health / Energy / Environment / Emergency
- Target: Adaptation
Implement grates at upstream entrances on the sewer network
Implementation of grates at the border between the rural catchment and the urban area to avoid coarse sediments and debris to get into the sewer.
- Category: Structural / Engineered and built environment
- Application Scale: River Basin
- Sector: Water
- Target: Adaptation
Implement monitoring system of the Climate Plan
Define and calculate the monitoring indicators for the Climate Plan
- Category: Non-structural / Government policies and programs
- Application Scale: City
- Sector: Water / Mobility / Telecom / Social / Power / Waste / Health / Energy / Environment / Emergency
- Target: Adaptation
Implement multi-hazard early warning systems
The implementation of an impact-based multi-sectorial warning system during an emergency case.
- Category: Non-structural / Government policies and programs
- Application Scale: City
- Sector: Water / Mobility / Telecom / Social / Power / Waste / Health / Energy / Environment / Emergency
- Target: Adaptation
Implementation of Rainwater Harvesting systems (RWH)
Rainwater Harvesting (RWH) is the collection of rainwater runoff for use. Runoff can be collected from roofs and other impermeable areas, stored, treated (where required) and then used as a supply of water for domestic, commercial, industrial and/or institutional properties.
- Category: Structural / Engineered and built environment
- Application Scale: City
- Sector: Water
- Target: Adaptation
Improve climate information on the resilience platform
Include a common repository of climate information on the resilience platform that ensures accessibility to all the players involved
- Category: Non-structural / Informational
- Application Scale: City
- Sector: Water / Mobility / Telecom / Social / Power / Waste / Health / Energy / Environment / Emergency
- Target: Adaptation
Improve flood forecasting
Enhance the flood forecasting and warning system of the city. It support the creation of awareness of neighbors and provides nformation to the citizens for them to take preventive measures in their homes
- Category: Non-structural / Government policies and programs
- Application Scale: City
- Sector: Water / Mobility / Telecom / Social / Power / Waste / Health / Energy / Environment / Emergency
- Target: Adaptation
Improve our knowledge on the effects of climate change on natural systems
Improve our knowledge of the effects of climate change on natural systems (phenology, allergies, pests, etc.)
- Category: Non-structural / Educational
- Application Scale: River Basin
- Sector: Environment
- Target: Adaptation
Improve public information about pollution
Improve the public information provided in pollution episodes and warnings of new risks
- Category: Non-structural / Informational
- Application Scale: City
- Sector: Social / Health / Environment
- Target: Adaptation
Improve the communication systems with critical city facilities and services during extreme climate episodes
Improve the communication systems with critical city facilities and services during extreme climate episodes
- Category: Structural / Technological
- Application Scale: City
- Sector: Mobility / Telecom / Emergency
- Target: Adaptation
Improve transparency on climate impacts through open data
Make public, through open data, relevant information on climate impacts and any monitoring action carried out (transparency)
- Category: Non-structural / Informational
- Application Scale: City
- Sector: Water / Mobility / Telecom / Social / Power / Waste / Health / Energy / Environment / Emergency
- Target: Adaptation
Improving protection schemes to integrate renewable energy
Implementation of new protections and communication schemes in medium and low voltage networks.
- Category: Structural / Technological
- Application Scale: City
- Sector: Telecom / Power / Energy
- Target: Adaptation
Incorporate CC criteria in the Special Plan for protecting the environment and landscape of the Serra de Collserola nature reserve
Incorporate CC criteria in the Special Plan for protecting the environment and landscape of the Serra de Collserola nature reserve
- Category: Non-structural / Government policies and programs
- Application Scale: City
- Sector: Environment
- Target: Adaptation
Increase digitalization, communication and automation of energy system
By increasing the digitalization of the system, more information of the status of the grid is collected. Remote controlled measures and communication standards will create smart grids.
- Category: Non-structural / Informational
- Application Scale: City
- Sector: Mobility / Telecom / Power / Energy / Emergency
- Target: Adaptation
Increase height difference between street level and ground floor level
Rain water is usually collected in streets. To reduce probability for surface water to enter buildings, the difference between street level and ground floor level can be increased. This way more water can be stored in the street profile without flooding the buildings.
- Category: Structural / Engineered and built environment
- Application Scale: City
- Sector: Water / Mobility / Social / Waste / Emergency
- Target: Adaptation
Increase integration of renewable energy by distributed generation
The decentralization of the distribution grid by placing renewable generating units at the low voltage level of the power system enhances the continuity of supply in case of the shutdown of a big generating unit. For example, in a climate emergency situation, domestic photovoltaic panels, batteries and electric-vehicles with V2G capability could provide back-up power, increasing resilience.
- Category: Structural / Technological
- Application Scale: Building
- Sector: Water / Mobility / Telecom / Social / Power / Health / Energy / Environment / Emergency
- Target: Adaptation
Increase pumping capacity
By increasing the pump capacity water tables can be controlled better. Responding to heavy rains becomes easier, and the chance of flooding is reduced. The need for buffer capacity, translated into low water tables in rivers and channels, is also reduced as the managers have more pumping capacity.
- Category: Structural / Engineered and built environment
- Application Scale: City
- Sector: Water / Mobility / Environment / Emergency
- Target: Adaptation
Increase soil permeability by defining a sustainable urban drainage strategy
Increase soil permeability by defining a sustainable urban drainage strategy for Barcelona that offers design recommendations in a manual, maintenance protocols (with professional training to ensure it is done correctly) and recommendations on how to monitor and evaluate its effectiveness using monitors and sensors
- Category: Structural / Ecosystem-based
- Application Scale: City
- Sector: Water / Social / Health / Environment
- Target: Adaptation